Florida’s zero tolerance law is implemented administratively. – Florida’s zero tolerance law is implemented administratively, sparking ongoing debates and controversies. This law has significant implications for students, educators, and the overall school environment. This comprehensive analysis delves into the complexities of this policy, examining its implementation, impact, legal challenges, and alternative approaches.
Florida’s zero tolerance law, enacted with the intent of enhancing school safety and reducing disruptive behavior, has garnered both praise and criticism. While it has been credited with deterring misconduct, concerns have been raised regarding its potential for over-criminalization and disproportionate impact on minority students.
1. Definition and Overview: Florida’s Zero Tolerance Law Is Implemented Administratively.

Zero tolerance laws in the context of education are policies that mandate strict and severe consequences for any violation of school rules, regardless of the severity of the offense. These laws were implemented in response to a perceived increase in school violence and disruptive behavior.
Florida’s zero tolerance law, passed in 1997, is one of the most comprehensive and far-reaching in the nation. The law applies to all public schools in the state and covers a wide range of offenses, including possession of weapons, drugs, and alcohol; assault and battery; and theft.
Specific Provisions and Consequences, Florida’s zero tolerance law is implemented administratively.
- Mandatory expulsion for any student found in possession of a firearm on school property
- Mandatory suspension for any student found in possession of a weapon other than a firearm
- Mandatory suspension for any student who assaults or batters another student
- Mandatory suspension for any student who steals property valued at $100 or more
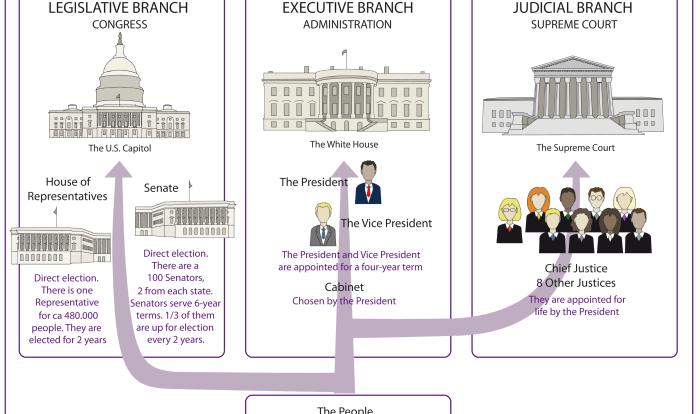
2. Administrative Implementation
Florida’s zero tolerance law is implemented administratively by school administrators and law enforcement officers. When a student is accused of violating the law, the school administrator will typically conduct an investigation. If the administrator determines that there is sufficient evidence to support the allegations, the student will be suspended or expelled from school.
In some cases, the school administrator may also refer the student to law enforcement for criminal prosecution. Law enforcement officers will then conduct their own investigation and may file charges against the student.
Key Stakeholders
- School administrators
- Teachers
- Law enforcement officers
3. Impact on Students

Zero tolerance policies have been shown to have both positive and negative effects on students.
Potential Benefits
- Reduced school violence
- Safer learning environment
Potential Drawbacks
- Disproportionate impact on minority students
- Potential for over-criminalization
Research has shown that zero tolerance policies are more likely to be applied to minority students than white students, even for the same offenses. This disparity is due in part to the fact that minority students are more likely to be perceived as being disruptive and threatening than white students.
Zero tolerance policies can also lead to the over-criminalization of student behavior. This is because these policies often mandate harsh punishments for even minor offenses. As a result, students who are suspended or expelled from school for minor offenses may end up in the juvenile justice system.
4. Legal Challenges and Controversies

Florida’s zero tolerance law has been challenged in court on several occasions. The most significant challenge came in 2000, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of a student who was expelled from school for bringing a knife to school.
The Court ruled that the school district’s zero tolerance policy was unconstitutional because it did not provide for any exceptions to the mandatory expulsion requirement.
In response to the Supreme Court’s ruling, the Florida Legislature amended the zero tolerance law to allow for exceptions in certain cases. However, the law has continued to be challenged in court, and there are several cases currently pending.
Arguments for and Against the Law
- Arguments for the law:Proponents of the law argue that it is necessary to reduce school violence and create a safer learning environment. They also argue that the law is fair and equitable, because it applies to all students regardless of their race or socioeconomic status.
- Arguments against the law:Opponents of the law argue that it is too harsh and that it disproportionately impacts minority students. They also argue that the law is ineffective in reducing school violence and that it creates a hostile learning environment.
5. Alternatives to Zero Tolerance
There are a number of alternatives to zero tolerance policies that have been shown to be effective in reducing school violence and creating a more positive learning environment.
One alternative is restorative justice. Restorative justice is a process that focuses on repairing harm and building relationships rather than on punishment. Restorative justice programs have been shown to be effective in reducing recidivism and in improving school climate.
Another alternative to zero tolerance is positive behavior intervention and supports (PBIS). PBIS is a school-wide system that focuses on rewarding positive behavior and providing support to students who are struggling. PBIS programs have been shown to be effective in reducing disruptive behavior and in improving academic achievement.
FAQ Corner
What are the key provisions of Florida’s zero tolerance law?
The law mandates automatic suspension or expulsion for a range of offenses, including possession of weapons, drugs, and alcohol, as well as physical altercations.
How does the administrative implementation of the law work?
School administrators have the authority to enforce the law and determine appropriate disciplinary measures, which may include suspension, expulsion, or referral to law enforcement.
What are the potential benefits of zero tolerance policies?
Proponents argue that these policies deter misconduct, promote a safer learning environment, and hold students accountable for their actions.
What are the potential drawbacks of zero tolerance policies?
Critics contend that these policies can lead to excessive punishment, disproportionately impact minority students, and undermine the educational mission of schools.