Amoeba sisters dna chromosomes genes and traits answer key – Amoeba Sisters DNA, Chromosomes, Genes, and Traits Answer Key provides a comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts of genetics, empowering learners with an in-depth understanding of the structure, function, and inheritance of genetic material.
This meticulously crafted answer key complements the engaging video lessons by Amoeba Sisters, renowned for their ability to simplify complex scientific concepts. By delving into the intricacies of DNA, chromosomes, genes, and traits, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking to expand their knowledge in genetics.
Introduction to Amoeba Sisters: Amoeba Sisters Dna Chromosomes Genes And Traits Answer Key
Amoeba Sisters is an educational YouTube channel that creates animated videos to teach biology and science concepts in a fun and engaging way. The videos are designed for students in grades 6-12, and they cover a wide range of topics, including cells, genetics, evolution, and the human body.
DNA Structure and Function

DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. It is made up of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The nucleotides are arranged in a specific order, which determines the genetic code.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells. It is organized into structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins. The proteins help to protect the DNA and to regulate gene expression.
DNA is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. When a cell divides, the DNA is copied so that each new cell has its own copy of the genetic code.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which DNA is copied. It occurs during cell division. The DNA molecule is unwound and the two strands are separated. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
The result is two new DNA molecules, each of which is identical to the original molecule.
Chromosomes and Genes
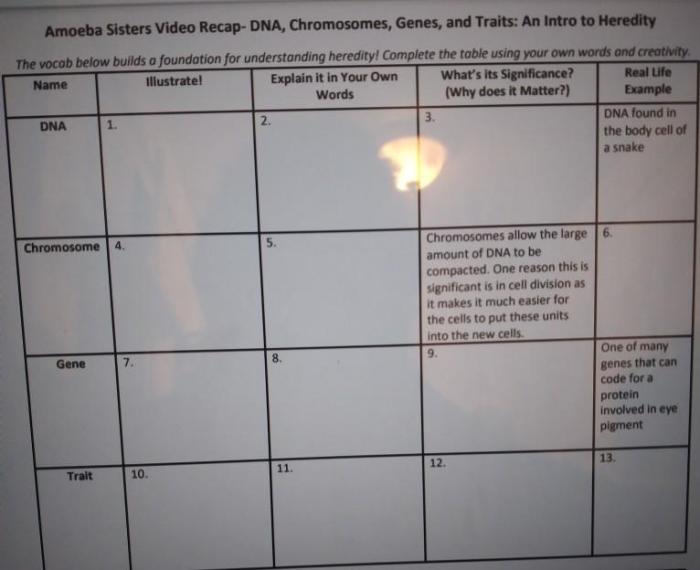
Chromosomes are structures in the nucleus of cells that contain DNA. Each chromosome is made up of a single molecule of DNA. The DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones. The histones help to protect the DNA and to regulate gene expression.
Genes are regions of DNA that code for proteins. Proteins are the building blocks of cells and they play a vital role in all cellular processes. Each gene codes for a specific protein.
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which the information in a gene is used to make a protein. The first step in gene expression is transcription. During transcription, the DNA is copied into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA then travels out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into a protein.
Traits and Inheritance

Traits are characteristics of an organism. They can be physical, such as eye color or height, or they can be behavioral, such as intelligence or aggression. Traits are determined by genes.
Inheritance is the process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring. Genes are passed from parents to offspring through chromosomes. Each parent contributes one chromosome to each offspring, so each offspring inherits half of their genes from their mother and half from their father.
Types of Inheritance Patterns, Amoeba sisters dna chromosomes genes and traits answer key
- Autosomal dominant inheritance: A trait is dominant if it is expressed in an individual who has only one copy of the gene for that trait. A recessive trait is only expressed in an individual who has two copies of the gene for that trait.
- Autosomal recessive inheritance: A trait is recessive if it is only expressed in an individual who has two copies of the gene for that trait.
- X-linked inheritance: A trait is X-linked if the gene for that trait is located on the X chromosome. Males are more likely to inherit X-linked traits because they only have one X chromosome.
Mutations
Mutations are changes in DNA. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to radiation or chemicals. Mutations can have a variety of effects, including changing the function of a gene or causing a gene to be turned off.
Mutations can create new traits. For example, a mutation in the gene for eye color could lead to an individual having blue eyes instead of brown eyes.
Amoeba Sisters Videos
- DNA Structure and Function: This video explains the structure of DNA and its role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
- DNA Replication: This video explains the process of DNA replication.
- Chromosomes and Genes: This video explains the structure of chromosomes and the role of genes in determining traits.
- Gene Expression: This video explains the process of gene expression.
- Traits and Inheritance: This video explains the different types of inheritance patterns and the role of mutations in creating new traits.
Expert Answers
What is the role of DNA in genetic inheritance?
DNA serves as the blueprint for genetic inheritance, carrying the instructions for all the traits and characteristics of an organism. It is passed down from parents to offspring, ensuring the continuity of genetic information across generations.
How do chromosomes influence gene expression?
Chromosomes are organized structures within cells that contain DNA. They play a crucial role in gene expression by regulating which genes are turned on or off, thereby determining the specific traits and characteristics of an organism.
What is the significance of mutations in genetic variation?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can introduce new traits or alter existing ones. They are a driving force behind genetic variation and evolution, contributing to the diversity of life on Earth.