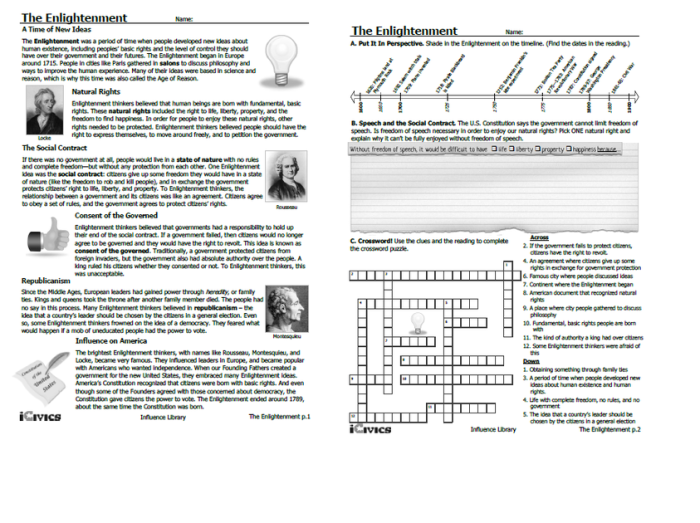
Embark on a journey into the realm of judicial review with our comprehensive guide, judicial review icivics answer key pdf. This document delves into the intricacies of this fundamental legal concept, empowering you with a profound understanding of its significance and practical applications.
Judicial review serves as a cornerstone of democratic societies, ensuring that the actions of government align with the rule of law. Through thought-provoking examples and in-depth analysis, this guide illuminates the multifaceted nature of judicial review, empowering you to navigate its complexities with confidence.
Definition and Overview of Judicial Review
Judicial review is the power of a court to examine the actions of the other branches of government and to determine whether those actions are in accordance with the constitution or other laws. It is a fundamental principle of constitutional law in many democratic countries, and it serves to protect the rights of citizens and to ensure that the government is accountable to the people.
Judicial review has been used in a wide variety of cases, including cases involving the constitutionality of laws, the actions of government officials, and the rights of individuals. In the United States, the Supreme Court has played a major role in shaping the doctrine of judicial review, and it has issued a number of landmark decisions that have had a profound impact on American law and society.
Process of Judicial Review
The process of judicial review typically begins when a person or group files a lawsuit challenging the constitutionality of a law or government action. The lawsuit is then heard by a court, which will decide whether the law or action is in accordance with the constitution or other laws.
If the court finds that the law or action is unconstitutional, it will issue a ruling that strikes it down.
Courts can grant a variety of different types of relief in judicial review cases. These remedies can include:
- Declaratory judgments, which declare that a law or action is unconstitutional.
- Injunctions, which order the government to stop enforcing a law or taking a particular action.
- Damages, which compensate individuals for injuries they have suffered as a result of an unconstitutional law or action.
Judicial Review in the United States: Judicial Review Icivics Answer Key Pdf
The doctrine of judicial review was first established in the United States in the case of Marbury v. Madison(1803). In this case, the Supreme Court ruled that it had the power to declare laws unconstitutional. This decision has been upheld in subsequent cases, and it is now considered to be a fundamental principle of American law.
The Supreme Court has played a major role in shaping the doctrine of judicial review in the United States. The Court has issued a number of landmark decisions that have had a profound impact on American law and society, including decisions on issues such as civil rights, freedom of speech, and the separation of powers.
Judicial Review in Other Countries
The doctrine of judicial review is not unique to the United States. It is also found in a number of other countries, including Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia. However, the scope and effectiveness of judicial review can vary significantly from country to country.
In some countries, such as the United States, judicial review is a powerful tool that can be used to strike down laws and government actions that are found to be unconstitutional. In other countries, judicial review is more limited, and courts are less likely to overturn the actions of the other branches of government.
Challenges and Criticisms of Judicial Review
Judicial review has been criticized on a number of grounds. Some critics argue that it gives too much power to judges, who are not elected by the people and who may not be accountable to the public. Others argue that judicial review is too slow and cumbersome, and that it can lead to delays in the implementation of important laws and policies.
Despite these criticisms, judicial review remains an important tool for protecting the rights of citizens and ensuring that the government is accountable to the people. It is a fundamental principle of constitutional law in many democratic countries, and it is likely to continue to play a vital role in the years to come.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of judicial review?
Judicial review empowers courts to examine the actions of government entities, ensuring that they comply with the constitution and applicable laws.
How does the judicial review process work?
Individuals or organizations can file lawsuits challenging government actions. Courts then review the evidence and legal arguments to determine if the government’s actions were lawful.
What are the different types of relief that courts can grant in judicial review cases?
Courts can issue a variety of remedies, including injunctions, declaratory judgments, and orders to compel or prohibit specific actions.